ONE NAME TO TRUST FOR BONE MARROW TRANSPLANTS
World Class Surgery and Care
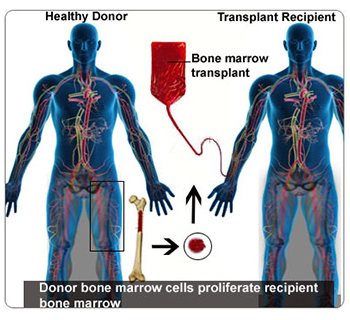
Bone Marrow Transplant in India
A bone marrow transplant is a procedure to replace damaged or destroyed bone marrow with healthy bone marrow stem cells.
Bone marrow is the soft, fatty tissue inside your bones. The bone marrow produces blood cells. Stem cells are immature cells in the bone marrow that give rise to all of your different blood cells.
How things function at Indo Med Consultancy
- 1. Qualified panel : Indo Med Consultancy has association with highly-efficient surgeons and doctors, a prerequisite in treating any medical condition
- 2. Primary facilities : We offer assistance in arranging medical visa, accommodation for the patient and family, meals, appointment with surgeon.
- 3. Cost-friendly : Financial aspects affect medical treatments in a huge way, and our budget friendly packages won’t burn a hole in your pocket.
- 4. Other services: We also take care of quick visa letter, health diet as advised by your attending surgeon, to and fro airport travel, vacation tour, etc.
What is Bone Marrow Transplant
Before the transplant, chemotherapy, radiation, or both may be given. This may be done in two ways:
- Ablative (myeloablative) treatment: High-dose chemotherapy, radiation, or both are given to kill any cancer cells. This also kills all healthy bone marrow that remains, and allows new stem cells to grow in the bone marrow.
- Reduced intensity treatment, also called a mini transplant: People receive lower doses of chemotherapy and radiation before a transplant. This allows older people, and those with other health problems to have a transplant.
Why the Procedure is Performed?
A bone marrow transplant replaces bone marrow that is either not working properly or has been destroyed (ablated) by chemotherapy or radiation.
Doctor may recommend a bone marrow transplant if you have:
- Certain cancers, such as leukemia, lymphoma, myelodysplasia, and multiple myeloma
- A disease that affects the production of bone marrow cells, such as aplastic anemia, congenital neutropenia, severe immunodeficiency syndromes, sickle cell anemia, and thalassemia
What Kind of Risks you have?
A bone marrow transplant may cause the following symptoms:
- Chest pain
- Drop in blood pressure
- Fever, chills, flushing
- Funny taste in the mouth
- Headache
- Hives
- Nausea
- Pain
- Shortness of breath
What are the Complications may include?
- Anemia
- Bleeding in the lungs, intestines, brain, and other areas of the body
- Cataracts
- Clotting in the small veins of the liver
- Damage to the kidneys, liver, lungs, and heart
- Delayed growth in children who receive a bone marrow transplant
- Graft failure, which means that the new cells do not settle into the body and start producing stem cells
- Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), a condition in which the donor cells attack your own body
- Stomach problems, including diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting
Before the Procedure
Before transplant, you will have one or two tubes, called catheters, inserted into a blood vessel in your neck or arms. This tube allows you to receive treatments, fluids, and sometimes nutrition. It is also used to draw blood.
Your provider will likely discuss the emotional stress of having a bone marrow transplant. You may want to meet with a counselor. It is important to talk to your family and children to help them understand what to expect.
You will need to make plans to help you prepare for the procedure and handle tasks after your transplant:
- Complete an Advance Care Directive(Living will; Power of attorney; DNR – advance directive; Do not resuscitate – advance directive; Do-not-resuscitate – advance directive)
- Arrange medical leave from work
- Take care of bank or financial statements
- Arrange for someone to help with household chores
- Confirm health insurance coverage
- Pay Bills
- Find housing for yourself or your family near the hospital, if needed
After the Procedure
A bone marrow transplant is usually done in a hospital or medical center that specializes in such treatment. Most of the time, you stay in a special bone marrow transplant unit in the center. This is to limit your chance of getting an infection.
Depending on the treatment and where it is done, all or part of an autologous or allogeneic transplant may be done as an outpatient. This means you do not have to stay in the hospital overnight.
How long you stay in the hospital depends on:
- How much chemotherapy or radiation you received
- The type of transplant
- Your medical center’s procedures
While you are in the hospital you may:
- Receive medicines to prevent or treat infections, including antibiotics, antifungals, and antiviral medicine
- Need many blood transfusions
- Be given medicines to prevent GVHD
Outlook (Prognosis)
How well you do after the transplant depends on:
- The type of bone marrow transplant
- How well the donor’s cells match yours
- What type of cancer or illness you have
- Your age and overall health
- The type and dosage of chemotherapy or radiation therapy you had before your transplant
- Any complications you may have
A bone marrow transplant may completely or partially cure your illness. If the transplant is a success, you can go back to most of your normal activities as soon as you feel well enough. Usually it takes up to 1 year to recover fully, depending on what complications occur.
Complications or failure of the bone marrow transplant can lead to death.

